The human resources management field not only include training, recruitment, performance and pay but also covers important legal issues. In today’s article, we will talk about the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) organizational chart with an example.
What is the Fair Labor Standards Act?
It is a United States federal law published by Congress in 1938 and it covers five parts: minimum wage, overtime pay eligibility, recordkeeping, and child labor. The Fair Labor Standards Act influence both full-time and part-time workers in profit and non-profit organizations. According to the Act, all overtime-eligible employees MUST be paid with overtime compensation for all hours worked more than 40 in a single week. Here is an example of the Fair Labor Standards Act org chart:

Know more about the Five Key Aspects of the Act
Fair Labor Standards Act Min. Wage
The FLSA determines a minimum wage standard for employers to follow. The current federal minimum wage is $7.25 per hour. Employers must pay their employees the highest amount between the applicable federal, state, and local min. wage.
Fair Labor Standards Act Overtime
This policy requires employers must pay overtime wages to their employees when an employee works over 40 hours a week unless they are exempt. Exempt employees are those who have executive, or administrative job duties. Overtime pay is 1.5 times their regular hourly rate. Additionally, the FLSA does not require overtime wage for work on weekends or holidays.
Hours Worked
This part normally covers all the time during which an individual employee is required to be on the employer’s premises. The Fair Labor Standards Act Hours Worked policy helps employers to decide and pay for the correct working hours of their employees. In reality, it is not easy to count all the working hours, but usually, the following cases should be included: meetings and training time, meal breaks, and on-call time.
Recordkeeping
The Fair Labor Standards Act recordkeeping regulation states that employers must maintain consistent and accurate records of their employees such as the following: name, social security No., address, hours worked each day, wage deduction amounts, weekly overtime earnings and many more.
Child Labor
The Child Labor Act is established to protect the educational opportunities of minors who are under 18 years old by limiting their work hours during school days. Furthermore, employers should offer suitable jobs to children according to their age and skills. Employers should carry out due diligence to gain more information before hiring minors.
Penalties of the Fair Labor Salary Act Violations
Employers will face fines depending on the specific case of the violation. For example, violating FLSA minimum wage and overtime laws may cause over $1,900 fine per employee; violating child labor standards may cause more than $56,000.
How to Create a Fair Labor Standards Act Organizational Chart?
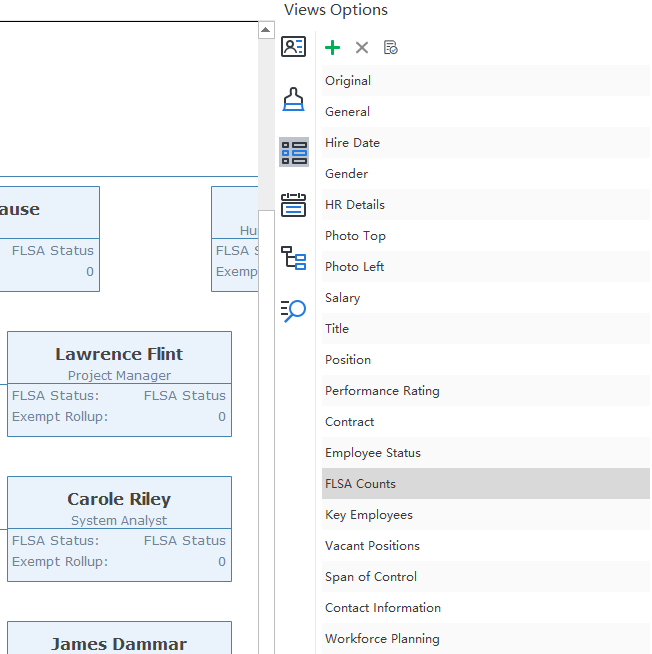
It’s more than easy to create your own FLSA org chart by using an easy org chart creator with advanced human resources management features. Simply click on the Views Options>FLSA Counts at the right-hand side your user interface. Next, you can double-click on any of the employee shapes to edit details.
Conclusion
In this easy guide, we have discussed the basic definition and the five key aspects of the Fair Labor Standards Act. It is also convenient to create a Fair Labor Standards Act org chart with a handy tool as shown above. Why not have a try right now?